ENTOMOLOGY 2040
SECTION VII
POLLINATION - HONEY BEES AND OTHERS |
 |
LEARNING OBJECTIVES OF SECTION
After completing this section students should be able to:
- Describe how the mutually beneficial relationships between insects and some plants may have developed.
- Describe the kinds of benefits that pollinating insects and their plant partners each get from the relationship.
- Explain how the color vision of honey bees may be related to the flowers they visit.
- Explain the differences between perfect and imperfect flowers and why both might require insect pollination.
- List the major groups of pollinators and explain which ones are most important, and why.
- Describe the plant and insect structural modifications that have evolved in the insect pollination relationship.
- Explain how solitary bees differ from their social relatives and why some are such effective pollinators.
- List the pollinator groups, other than Hymenoptera, and rank them in order of importance.
- Pollination - Honey Bees and Others.
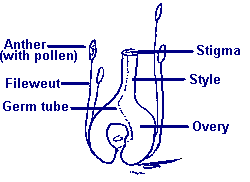
- 1. Flower structure.
- a. Pollination vs. fertilization.
- b. Perfect flowers vs. imperfect flowers.
- c. Plants.
- (1) Dioecious - male or female.
- (2) Monoecious - male and female.
- 2. Coevolution - plants and insects.
- a. Early flowers.
- b. Insect bumblers.
- c. Directed visitation.
- d. Plant adaptions.
- (1) Showy flowers--shapes and colors.
- (2) Landing platforms.
- (3) Tripping mechanisms.
- (4) Nectar guides.
- e. Insect adaptions.
- (1) Hairy bodies.
- (2) Diet.
- (3) Flower constancy.
- (4) Corbicula.
- (5) Mouth Parts.
- (6) Communication.
- 3. Importance of pollination.
- a. Crops.
- b. Pollinators.
- (1) Hymenoptera.
- • Honey bees.
- • Bumble bees.
- • Solitary bees.
- (2) Lepidoptera.
- • Hawkmoths.
- (3) Diptera.
- • Hover flies.
- • Bee flies.
- (4) Coleoptera.
STUDY QUESTIONS
- Describe the structural modifications that have occurred in plants that act to facilitate insect pollination.
- Describe the structural modifications that have occurred in insects, especially Hymenoptera, that facilitate pollination of certain flowers.
- Describe some behavioral and physiological that Hymenoptera have made that facilitate plant pollination.
- What is the difference between self pollination and cross pollination? Which do you think would be the "safer" strategy in insuring pollination.
- Describe some mechanisms that have evolved in perfect flowers that act to insure cross pollination.
- What is flower constancy? What is the value to the plant? To the insect pollinator?
- What do you think is the major value of cross pollination?
- What would be the effect of totally eliminating insect pollinators from the earth?
- What is the basic difference between social and solitary bees?
- What insect groups, other than Hymenoptera, are important pollinators? Which ones do you think would be most important?.

